What is worldwide education
Global Access to Education
Learning and Teaching Across Cultures
Recognising the importance of integrating global and multicultural approaches in the core of learning and teaching.
Promoting understanding and tolerance towards others’ cultures.
Internationalisation of Education
A Competitively Globalised Society
Focus on building global capabilities, including intercultural communication, problem-solving and adaptability.
Enabling learners to meet global challenges posed through changing climate, new technology, and growing social and economic disparities.
The Role of Education Technology in Reforming Educational Gaps
Utilising technology to eliminate the barriers created by distance especially for learners in difficult to reach or marginalised regions.
Online education platforms such as MOOCs and virtual classrooms enable students from various regions of the world to benefit from effective teaching.
Global Citizenship Education
Nurturing students so that they do their tasks with the knowledge and awareness of the issues faced globally.
Inviting youth to engage in actions for global peace, sustainability, equity, and social justice
What is worldwide learning

Building Understanding Across Borders
allows individuals and communities around the globe to create, exchange, and apply knowledge for the benefit of mankind. This goes beyond formal schooling to include informal and experiential education, online interaction, and cooperation across various facets of society. Worldwide learning is necessary in countering global issues, promoting inclusion, and equipping people with the necessary skills to be part of the global community in the future.
Worldwide learning is oriented towards and values the inclusion of all individuals in the educational process and the exchange of knowledge, but not at the expense of ontological self-determination. Mobile learning also employs technological tools, allows for intercultural communication, and uses international connections migrating from regional and national learning paradigms. This integrated approach includes:
High levels of technological development have expanded information access to the masses. The advent of the internet and other digital means makes it easy for even individual or regional outcasts to acquire educational materials. Solutions such as MOOCs, OERs, and many educational non-profits aim to change the lines of access and quality forever.
In addition, expanding the arc of cross-cultural dialogue, recognising and respecting the cultures of other countries can multiply their creative potential. With student exchange programmes, border projects, and global citizenship education, learners are exposed to cross-cultural perspectives and ideas and learn new ways of addressing problems.
Humanity across the world has to grapple with numerous issues today, such as climate change, public health, advancements in technology, among others. These require solutions that transcend mono-disciplinary focus. International education promotes synergy across disciplines and countries which consequently leads to effective solutions.
Worldwide Learning Components
Worldwide learning is comprised of a few components that are significantly interlinked with each other in order to form an integrated global education.
Technology Enhanced Learning
The learning revolution can be regarded as the flagship component of worldwide learning. The education sector has unraveled new avenues through online learning platforms such as MOOCs, e-learning, and apps. For instance:
- Platforms like Coursera, edX, and Khan Academy provide students around the world access to educational content through cheaper or free courses from reputable universities.
- Combined with VR and AR techniques, it allows students to learn in a realistic setting, such as witnessing the past, the unknown world, or some scientific phenomena.
Language is undoubtedly a key element of society, and international education embraces students with various languages. The Erasmus+ programme in Europe and the domestic USA college students with Fulbright scholarships help people study in foreign countries, learn languages and cultures directly.
This vision of Global Citizenship Education (GCED) is implemented in many countries within the framework of the initiative led by UNESCO. This initiative aims to develop students’ understanding of their place within an extended global community and takes the following form:
- Sees Human rights and social justice as key.
- Peace and conflict resolution.
- Sustainable development and climate action.
Worldwide learning targets the concept of fairness. It intends to bridge this gap through combating structural injustices so that disadvantaged groups such as girls, refugees, or individuals with disabilities can have a chance to learn.
Benefits of Worldwide Learning
The impacts of worldwide learning do not stop only at broadening individuals but also extend to communities and the entire world.
Learning is one of the tools that are important to one’s life, and regardless of one’s place or income, worldwide learning enables them to have the tools that are important for improving or enhancing their skills and career. It encourages continuous learning which enables individuals to keep up with the shifts in industries and technologies.
Fostering Global Collaboration
Worldwide learning enables individuals to feel part of the globe’s community due to its integration of learners and teachers from different backgrounds. Most of the time, international cooperation gives rise to new solutions to the world’s problems, such as new medical technologies or ways to make the economy more sustainable.
Living in such places expands horizons and brings about kindness, social awareness, and tolerance. This is important now as it always was: for world geopolitical instability and cultural misunderstandings often serve as a catalyst for war.
Education is one of the central aspects in reaching Sustainable Development Goals set by the United Nations. Special SDG 4 – Quality education is the main focus of worldwide learning, while other goals such as the promotion of gender equality, lower inequalities, or climate action are contributing factors to worldwide learning.
Language comprehension
The global outreach of educational programmes often suffers due to different languages. While such translation and multi-language support comes with certain technologies, the issue of inclusiveness in a world with thousands of languages is rather difficult to achieve.
Approbation of a custom
Global education or global learning programmes tend to look and feel superior, as there is always an aspect of a ‘baseline’ bullied narrative or a value. It is important to be cognisant of the local customs and knowledge systems in order to provide a global educational experience that is effective and not a power-centred one.
Economic reasons hold power even when the resources are there and they have to participate in learning at an international level. It is rather important to have scholarships and financial aid programmes in order to mitigate such inequalities.
Global Learning is also shaped and supported by institutions like governors, educational organisations, and private companies; as such players do contribute by:
Governments should in relation to education develop policies that seek to encourage and enhance global exchange in education by provision of resources such as financial assistance for foreign exchange and investment schemes for digital resources.
Partnerships and Alliances
In this sense, joint efforts of the universities with non-governmental bodies and organisations as well as the private sector can promote innovation and broaden the scope. It can be exemplified that cooperation between the institutions from developed and those from developing countries mostly enables cross border access to resources and expertise learning.
Educational research provides an avenue of how certain things are done for global learning to be purposeful at all times. All these and more are institutions like, UNESCO, the OECD, the World Bank.
The Future of Worldwide Learning
The advancement of technology in the future is limitless as far as endeavours of worldwide learning are concerned. Some examples of the new trends include:
With AI tailored tools integration, the content can be translated into many languages and the user learning speeds can be taken into consideration.
The use of blockchain in education can revolutionise it by making it possible to store and transfer academic credentials in a safe and transparent way.
Working with the global knowledge network can empower people during this challenging time when climate change is worsening, so they can come up with and implement effective solutions.
Worldwide learning represents the vision of a globalised world where information is at everyone’s disposal and education is able to unite people, fields of study as well as countries. Since knowledge knows no borders, teachings extend beyond regions and transform lives through advancing communication, integration, and creativity. Given the pressing circumstances, it is undeniable that for the advancement of humanity towards a better world, global learning must be adopted.
What are the values of global education

The Values of Global Education: Establishing Standards of an Integrated World
In essence, global education facilitates the endeavours of an individual to participate and engage with the world as a single entity. It encourages active efforts to respond and make contributions towards resolving worldwide issues while promoting values that are beyond borders. The principles gained through global education are those that promote values of empathy, respect, equity and sustainability which in turn promote responsible citizenship.
In this article, we analyse the key principles of global education and their role in an individual and society in an increasingly globalised environment.
Interconnectedness and Unity
In fact, one of the core principles of global education has to do with creating a sense of connectedness. This helps the learners realise that the world is a complex network of relationships, be it economic ones, cultural ones, environmental, or political. This outlook goes on to instil:
- Global interdependence: Magnifying the aspect where actions done in one corner of the globe will have impact in another corner of the globe.
- Common humanity: Focusing on shared issues of the environment, of poverty, health which should be handled in unity.
As global interdependence is instilled, learners also gain deeper understanding of unity and willingness to work together towards resolutions of global challenges.
Respect for Differences
Global education is an advocate of cultural, linguistic, and ideological respect as it trains the learners to view differences as strengths rather than barriers. This value encourages:
- Cultural Knocks: Raising awareness that life is not just one culture but many and the importance of understanding and integrating some views and ideas.
- Acceptance and belonging: All different types of units are different in acceptance and representation, which should be cherished and embraced.
Promoting diversity would create a society that would enhance peace, creativity, and collaboration across multiple cultures.
Sympathy and Empathy
Students developed possibilities by delivering global education sympathies that allow them to switch roles and view the developments of the globe from various angles. With this value people would be able to understand:
- Global disparities and unfairness.
- People are standing to support justice and amplify the voice of the voiceless.
- Share love and uphold each other in and out of work, politics and life generally.
Education that focuses on the social issues such as sympathy would eventually lead to the development of a true world where people respect and care for each other regardless of distance.
Fairness and Justice
Whilst addressing unfairness and tackling inequities is also one of the core values of global education. It entails empowering people to tackle unfairness and dealing with the existing disparities. For example,
- Gender fairness: Equal opportunities without limitations of any gender to teach, work, or engage in society.
- Equity – Understanding the gap between people with rich vs poor and doing something about such poverty.
- Social justice – Addressing injustices perpetrated against people due to race, ethnicity, religion and other such reasons.
The need for making equal opportunities to all and every individual is stressed upon through education so that society becomes equitable.
- Sustainable development – Pursuing economy and growth while also caring for the environment.
- Take climate action – Guiding students of all ages to become greener and to support initiatives that combat climate change.
- Conservative ethic – Preserving biodiversity and natural resources important for upcoming generations.
All these things can be derived through global education as well – a fundamental appreciation of the world and the society serves as a responsibility for its protection.
Critical Thinking and Open-mindedness
Global education fosters in students the readiness to examine assumptions, evaluate information, and solve problems from diverse vantage points. Such value furthers:
- Informed decision making – Routine bringing people a step closer to appreciating the foreign aspects of a mall though presents issues.
- Curiosity – Nurturing the interest in the world around, changes, other ways of living and thinking.
- Open-mindedness: Promoting acceptance of differences in opinion and constructive engagement.
Students are critical thinkers because they are expected to deal with the most urgent issues and survive in the conditions of volatility.
Peace and Conflict Resolution in the Context of Global Education
People who can settle disputes peacefully and help create a more peaceful world are of great importance. Global education provides for:
- Nonviolence communication: Imparting the ability to handle arguments without physical violence.
- Diplomacy and mediation: Giving learners basic skills of bridging gaps in families, communities, and international relations.
- Negative conflict transformation: History participation in campaigns that prevent the outbreak of conflict and promotes peace in the aftermath of it.
In developing the respect for peace, global education also helps create a more peaceful and united world order.
Global Responsibility in the Context of Global Education
Global education encourages to bear the responsibility of helping others and the world. It emphasizes:
- Participatory democracy: Demanding students to be involved in the affairs of the state and community.
- Socially responsible leadership: Keeping in mind the interest of all instead of a select few.
- Global awareness: Framing the mind to ensure commitment to raising such campaigns like human rights, environmental safety and social justice.
It is this sense of responsibility that makes sure that education is not only for personal achievements but for society as well.
Collaboration and Teamwork
Global education brings with it the focus on united efforts aimed at achieving common objectives. It appreciates:
- Project Initiation: Enhancing relationships with people from diverse nations and different cultures.
- Cooperative Plans of Action: Harnessing the collective energy of the people to find solutions to global problems.
- International Relations: Developing connections and relations across different nations.
Collaboration deepens relations around the globe, spawns creativity, and helps to develop appropriate solutions that work for everyone.
Lifelong Learning
With the changing times, global perspective stresses on the need for learning to be a never-ending process. This way of thinking enables a person to:
- Accept and deal with the changing circumstances: Remain in touch with the industries and society that is in flux.
- Have the zest for betterment: Always putting an effort to learn something new for self-growth and professional development.
- Be updated: Know what’s happening in the world, such as, changes and innovations so as to contribute positively.
Indeed learning which lasts a lifetime is indispensable for building flexibility and adaptability in the ever-shrinking world.
The Role of Educators in Promoting Global Values
As educators impart knowledge, they have been entrusted with the task of instilling the principles of global education. These principles can be put into practice in the course development and teaching practice in order to:
- Equip the students with skills which foster inclusivity in the learning process.
- Use real life scenarios to explain the global issues.
- Facilitate thoughtful debates, and expose students to cultural interactions, service learning or the practice of encouraging learning experiences outside the classroom.
Obstacles to the Development of Global Education
Nonetheless its significance, global education is not devoid of problems:
- Inequalities in resources: The ability to offer quality global education is sometimes limited within some geographical areas due to factors such as economic and infrastructural.
- Problems of change: Certain global views may be rejected by some communities due to political or cultural issues.
- Issues of over-emphasis on standardization: It may be difficult to reach a fair compromise between local educational requirements and the global aspirations of educators.
To deal with these challenges calls for partnerships between governments, organisations and educationists on a global scale.
Final thoughts
The purposes of global education provide the basis for the creation of a more equitable, just, and sustainable world. Global education facilitates the ability that enables individuals to be inter-related, respect diversity, be compassionate, and strive for justice and fairness, equipping citizens with the abilities required for the 21st century. It gives them the ability to be global citizens who make meaningful change in society and the wider world. Given the challenges created by globalisation, these values are pivotal for the creation of a better world for all.
What are the main values education
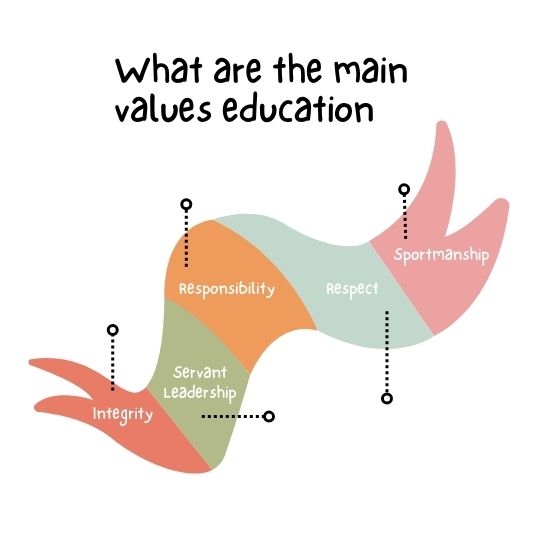
The Endearing Elements of Education: Character Development and Societal Advancement
Education is not just about the impartation of knowledge and skills. It can be applied to the individual learner and to society. Education instills values because at the heart of education, values are what motivates deeds, decisions and engagement. Those values that are critical for living a meaningful and ethical life help people to be in a position to offer something constructive towards their communities and the bigger society.
The aim of this essay is to highlight the core virtues of education and bring out their relevance towards the individual and the society.
Those Who Are Educated Should Show RESPECT
The greatest emphasis among educated people is respect. Educational values can be developed through self-work that also involves respect towards the individual, others, authority, and the environment. Education is able to nurture respect in a few ways.
- Self-respect. This notion labels students as people who have dignity, capability, and worth.
- Respect for others. Comparing someone against their own uniqueness, no matter their history, views or skills.
- Respect for authority and rule. These are factors that guide and allow for the reason and logic of a system to prevail amongst the population.
- Respect of the environment. Caring goes beyond one’s immediate love, desire or hope. People must be taught to appreciate everything from pollution to sustenance.
Having respect in place allows the educators to develop love that promotes respect among fellow human beings.
Education promotes self-responsibility and since people are capable of taking ownership of their actions, self-responsibility can be practiced in people as early as their school age. There are different forms in which responsibility can be learned:
- Personal Responsibility: A traditionally held view that people should be responsible for their actions and behaviours.
- Social Responsibility: The ability in people where they engage in activities and other programmes that promote the health and privileges of the society.
- Environmental Responsibility: Having a feeling of decency that drives one to take care of the environment and its components.
It is the responsibility of this responsible individual to imagine what a better world would look like and do the best within their power to make it happen.
Integrity is also considered to be a significant factor in the list of core values which education intends to grow within people. This can be described as a virtue which encompasses a firm commitment to moral and ethical convictions, even in difficult situations. In this regard, the education system encourages integrity in three areas:
- Honesty in all the academic works including but not limited to plagiarism and cheating.
- Encouraging openness and impartiality in relations with others.
- There is a need for a trait where one has beliefs and principles and is willing to defend them.
An education that encourages the development of integrity brings about trustworthy individuals who are dependable.
Empathy—the capacity to comprehend and participate in the emotions of others—is another core value that education should strive to cultivate among students. It, therefore, helps learners to do the following:
- Develop healthy social connections: Relating to people on an emotional level.
- Conflict management: Aldworth Jill, Healing Conflict: An Impact Evaluation of the Mediation Programme, explains how conflicts can be managed in a non-violent and humanistic manner.
- Support others: Providing assistance and comprehension with individuals in need.
Empathy is learned through education and thus makes society more caring and helpful.
Critical Thinking
Education is a major tool that encourages critical thinking, defining it as the ability to analyse, think outside the box, and be solution-oriented. This value is essential for:
- Making rational choices: Allowing people to be independent thinkers and assess situations and subsequently come to logical decisions.
- Encouraging new ideas and solutions: There is beauty in unorthodoxy and creating systems outside the box.
- Toughness: Cultivating learners who can face educated and reasonable approaches to situations and challenges.
With these skills, individuals are trained to dwell along the complexities of life in the current generation.
Equality and Fairness
Lessons on equality and fairness are core pillars within education. They are the tenets of justice and ensuring everyone has a fair chance within the prospects of the opportunities available to all. These values are the core focus of:
- Addressing discrimination: Such as those on the basis of race, gender, religion, or socioeconomic status.
- Inclusivity: This focuses on creating a support system where all students feel included.
- Equity: Providing equal treatment to people, especially those in disadvantaged situations and need the most.
When taught the right webs of equality and fairness through education, societies are developed with the ethos of diversity and inclusion embedded.
Hard work
The willpower or the faith to face challenges to accomplish goals is one worthy value that education strives to teach. In relation to hard work, students acquire:
- A growth mentality: That makes them resilient to difficulties and pushes them to keep looking for options.
- Persistence and determination: They foster the need to put in persistent efforts.
- Self-assurance and self-reliance: Which teaches students that with enough work, they can achieve their goals.
As a technique of strengthening oneself, perseverance ensures that every person strives to realise their dreams.
Working together
Working together posits that, for certain tasks with common objectives, the division of labour is essential. Education promotes teamwork through:
- Participation in students’ group work as well as group-shared learning.
- Respecting people’s views and their right to express them.
- Showing how many heads are better than one.
Carried out in education, students learn to appreciate the meaning of working together for the development of sound communities.
Self-directed learning
Lifelong learning encompasses the quest for knowledge and self-enrichment. Education, in this context, facilitates this by:
- Awakening inquisitiveness and the need to understand.
- Stressing the importance of being moulded as someone capable of adapting to changing times.
- Making learners explore on their own even after completing their formal education.
Those who are lifelong learners will have more flexibility in adjusting to changing times and will be able to further develop society.
Education is one of the significant mediums for establishing peace. It advocates for non-violence, conflict resolution, and coexistence. The following are key points:
- Encouraging tolerance: It is important to minimise bias and intolerance while cultivating compassion and understanding across peoples and faiths.
- Training in disagreements: People should be equipped with ideas or strategies that can be employed in addressing conflicts.
- Promoting global citizenship: Students should be motivated to participate in campaigns concerning social justice and human rights.
Peace education is about every individual learning to construct a world that is respectful and understanding of others.
This is an ethical value which is slowly gaining popularity in education. It prompts one to act in a manner that is resource-saving and mindful towards the next generation. Education achieves this by:
- Compelling students to realise how their actions affect the earth.
- Practising recycling and conservation to save the Earth.
Once again, appreciation for what one has or gratitude, which forms the core essence of education, is a strong value. It develops a positive mindset by:
- Helping learners to appreciate the work of other people.
- Creating satisfaction and also minimising acute thirst for material goods.
- Instilling the principles of gratitude and generosity.
Gratitude is a practice that fosters emotional health and enhances interpersonal relationships.
How Educators Can Aid in Teaching Values
Both intentionally and sometimes unwittingly, educators are fundamental in the transmission of values in a variety of ways as:
- Role modelling: One’s behaviour serves as a demonstration of the values of respect, empathy, and integrity.
- Teaching with values: Narratives, discussions, and examples from real-life scenarios to instil morals.
- Facilitating reflection: Where the emphasis is to help the student examine the relationship between his or her actions and the valued ends.
Teaching of Values New Approaches and Practices
Education based on values is very important, but this particular form of education must deal with a number of challenges, which include: –
- Clash of traditions and customs: Different cultures and societies esteem different values, so teaching methodologies become cumbersome.
- Priority differences: The emphasis in most cases is more on passing exams than developing one’s character.
- Implementation shortcoming: Children from poor socio-economic backgrounds tend to attend schools that do not implement sponsored values accordingly.
These challenges require concerted efforts from policymakers, teachers of education, and the community at large

